Institut Charles Sadron News
Publié le 11/06/2024 par Drenckhan Wiebke
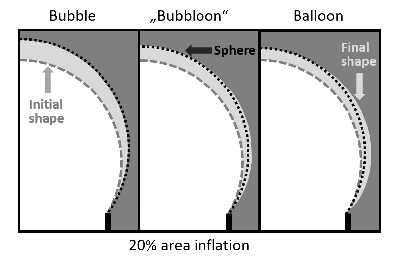
Fluid objects bounded by elastocapillary membranes display intriguing physical properties due to the interplay of capillary and elastic stresses arising upon deformation. Increasingly exploited in foam or emulsion science, the mechanical properties of elastocapillary membranes are commonly characterised by the shape analysis of inflating/deflating bubbles or drops held by circular needles. These impose complex constraints on the membrane deformation, requiring the shape analysis to be done using elaborate numerical fitting procedures of the shape equations. While this approach has proven quite reliable, it obscures insight into the underlying physics of the problem. A collaboration between the TSP and MIM team of the ICS has now established the first fully theoretical approach to this problem using the elastic theory for a membrane with additive contributions of capillary and Hookean-type elastic stresses. This work has been published in Soft Matter. The researchers exploit this theory to discuss some of the key features of the predicted pressure-deformation relations. Additionally, they provide an analytical relationship which will allows experimentalists to obtain the elastocapillary properties of a membrane by simple measurements of the height and the width of a deformed bubble (or a drop) on a needle.